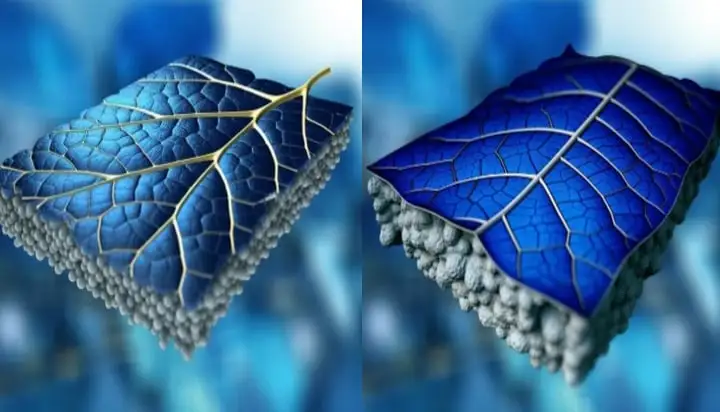
If anyone wants to read the actual details, there is a link in the article to a more-detailed one on nature.com: https://www.nature.com/articles/s41467-023-38984-7#Fig1
I kinda skimmed it. So from what I understand, they put a cooling layer behind regular solar panels. Panels get less efficient when they heat up so keeping them cool is where the extra efficiency comes from. The cooling layer is inspired by how plants cool themselves, it seems sort of similar to sweating in a way. Water moves through by capillary action, absorbs heat from the panel, and evaporates. Additionally they discuss:
- using salt water as input water, which will result in some clean water output. It seems you need to kinda flush the cooling layer at night to get rid of salt crystal build up, but this could be a nice bonus in less developed areas.
- use a condenser down the line to recover heat energy from the evaporated output water. Has the potential to raise total efficiency by a bunch of you can use the warm water for heating and the PV generated electricity for power.
They claim the cooling layer doesn’t add much extra cost (6 months extra operation to recoup your investment). I wonder what the lifetime of the cooling layer is compared to the photovoltaics themselves. They use some natural fiber I think so maintenance could be an issue.
This article has as much substance to it as a saltine cracker.
I think you’re underselling the substance of a saltine. This felt like a bad AI generated piece.
The cracker is more useful but it is very thin and mostly air, but fair enough.
It has the substance of a saltine cracker with 0 sodium.
“leafs”? Really?
ikr, the correct form is in the article as well…
Experiments reveal PV-leaves generate over 10% extra electricity compared to standard solar panels, which dissipate 70% of solar energy.
Edit. Maybe it’s pedant bait
on one hand I agree that it’s an embarrassing error.
On the other hand, what in the flying fuck is the reason to have leaves as the plural form of leaf over leafs.
Knives, lives and wives too, but why not roofs and chiefs? Is it hoofs or hooves?
Mices
Hockey fan from Toronto probably
Experiments reveal PV-leaves generate over 10% extra electricity compared to standard solar panels, which dissipate 70% of solar energy.
So basically you go from using 30% of solar energy to 33%? Sounds nice but would that really do that much?
It’s not just a 10% increase in productivity, it produces fresh water as a byproduct:
Furthermore, the photovoltaic leaf is capable of synergistically utilising the recovered heat to co-generate additional thermal energy and freshwater simultaneously within the same component, significantly elevating the overall solar utilisation efficiency from 13.2% to over 74.5%, along with over 1.1 L/h/m2 of clean water.
where does the salt go? wouldn’t it build up in the pipes and cause them to get clogged?
Another commenter summarized the nature article linked in comments… Yes, the salt is left in the pipes, so they are flushed out at night to prevent buildup.
1.1l/h/m2 ? That means 25m2 generate 27.5l/h so 660l a day. That’s huge.
You’re assuming full production for 24 hours a day, I don’t think that’s likely. Maybe 8 hours of full production a day under optimal conditions? Still, ~200 liters a day of potable water seems quite big for a 5x5 area of solar panels.
Yeah, my bad. Your estimate seems more likely.
Thats pretty cool, although that is not even mentioned in the article unless Im missing something.
The article is extremely light on detail
That bleeping lobster linked the actual paper
It doesn’t make sense to think of it in terms of how much of the Sun’s energy it uses because solar energy is essentially free and unlimited, it comes from an outside system, we don’t need to mine it or carry it or anything and we can’t ‘waste’ it in the same way we can other fuels. All it tells us is the maximum theoretical limit.
10% more energy from solar means a rooftop array could generate an extra 300-500W which is a genuinely useful amount of energy.
deleted by creator